Consent forms the bedrock of our society, empowering individuals to make informed choices and ensuring that actions are taken willingly and voluntarily. This article explores the critical role of consent in preserving freedom and autonomy, drawing attention to its significance in various contexts.
Consent: Empowering Yes and No
Consent is a crucial concept that forms the foundation of our society. It ensures that all parties involved are aware of and agree to their actions willingly. Consent empowers individuals to say yes or no, and it is essential for freedom and autonomy. Without consent, we risk becoming victims or losing our freedom.
An example that highlights the importance of consent is the distinction between robbery and a transaction. In a robbery, the victim is forced to surrender their belongings against their will due to the threat of violence. In contrast, a transaction occurs when both parties willingly agree to exchange something of value. Consent is what makes the transaction valid. Without it, the exchange becomes an act of robbery.
Consent in Employment: Preserving Autonomy
Similarly, consent plays a significant role in differentiating between slavery and employment. In slavery, individuals are coerced into work without their consent, often through threat of harm or violence. By contrast, employment involves an agreement where a worker willingly agrees to perform tasks or services in exchange for compensation. Consent is the crucial factor that preserves the worker’s autonomy and freedom in an employer/employee relationship.
Sovereignty: Rules and Cooperation
Sovereignty arises from a combination of rules and cooperation. Rules establish the structure of a society, defining the rights and obligations of individuals and institutions. In a free market, rules emerge over time. These rules ensure fair competition and the voluntary exchange of goods and services based on mutual consent.
Voluntary cooperation among individuals leads to the creation of value and the development of trust. This collaborative effort has given rise to the demand for new and better forms of money that are rooted in cooperation rather than coercion. Such emergent monetary systems are market-driven and founded on mutual agreement, rather than the traditional top-down systems enforced through coercion and violence.
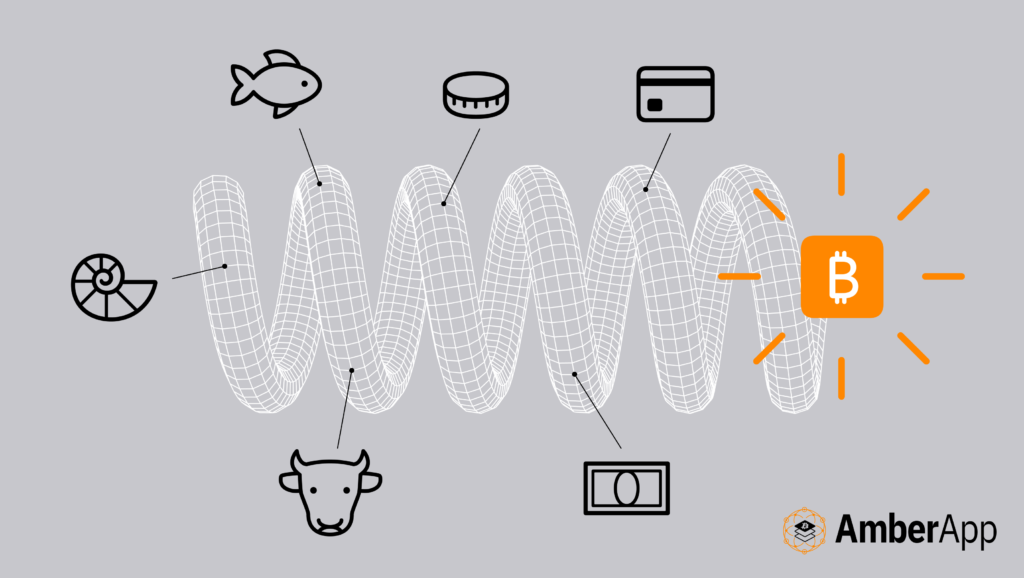
Market-Founded Money: A Cooperation-Based System
Throughout history, different commodities such as Yap stones, tally sticks, precious metals, and Bitcoin have served as market-founded forms of money. In contrast, authoritative money, like unbacked paper or digital currencies imposed by central banks, is mandated by government and legal systems and subject to arbitrary rules that can change over time. This inconsistency makes it challenging for users to plan for the future or accurately measure the value of goods and services over time.
The Consequences of Disregarding Consent: Loss of Freedom
When individuals are victimized or enslaved, it is usually due to rulers who disregard the importance of consent. These rulers employ threats of violence to coerce, expropriate, and steal from others. The varying degrees of control exerted by rulers can be compared to different levels of slavery, but the fundamental question remains: Can one freely say no or not?
Rulers exploit their power to impose their will, often justified by claims of “safety” or “protection.” This results in a loss of freedom and autonomy, as individuals are compelled to comply with the ruling class’s directives or face consequences such as fines or imprisonment.

Centralized Control and Fiat Currency
Fiat currency, which relies on government enforcement through legal tender laws, is a poor form of money that would not be chosen or consented to, if given the option. When individuals are forced to use a specific currency, their ability to choose is restricted and they become subject to the control of those who govern the currency.
This centralized control can lead to economic instability, as the value of the currency is not based on voluntary cooperation and trust. Countries like Zimbabwe, Lebanon, Venezuela, and Argentina provide examples of monopolized currencies that erode people’s savings, disrupt their ability to plan for the future, and redistribute purchasing power.
Conclusion: Upholding Consent for Freedom and Autonomy
In summary, consent serves as the cornerstone of freedom and autonomy in various aspects of our lives. It empowers us to maintain control over our decisions, values, and beliefs, whether in personal interactions or business dealings. Without consent, we risk becoming powerless victims or slaves, subjected to the arbitrary whims of others. By establishing a society built on a combination of rules and voluntary cooperation, we can foster an environment that upholds consent, promotes freedom, and safeguards individual autonomy.
Do you want to learn more about how you can use Bitcoin as a store of value and hedge against legacy financial and economic systems? AmberApp makes it easy for you to start sacking sats in minutes.
Download AmberApp and make your first Bitcoin purchase in under 90 seconds.






