Introduction
Centralisation, whether in governance or money, is a concept that entails the concentration of power and control within a single entity or a select group. This article explores the intricacies of centralisation, considering both its positive and negative aspects. Additionally, it delves into the impact of centralised control over money, its historical development, and the theoretical and practical implications it poses.
Centralisation in Governance
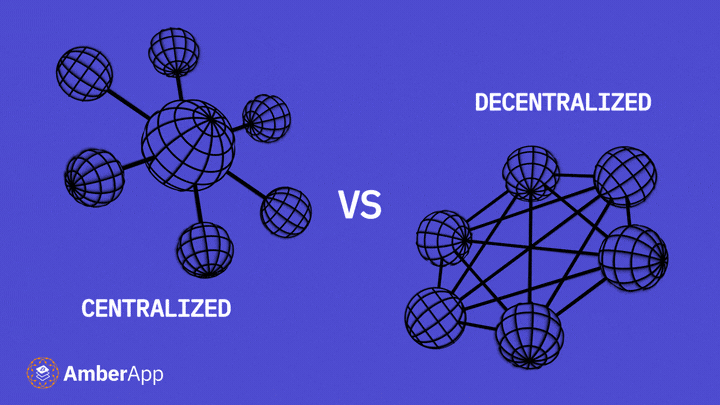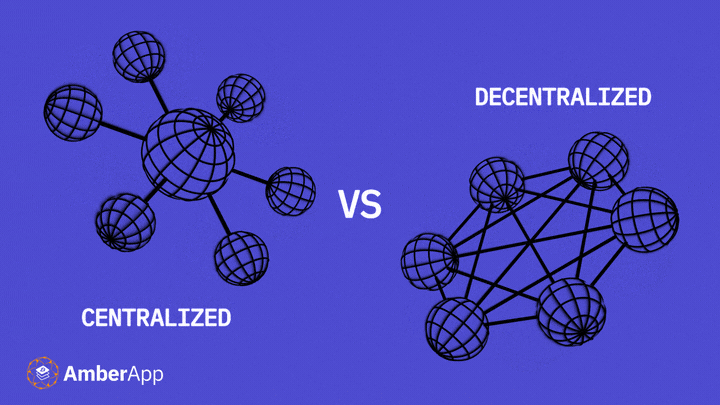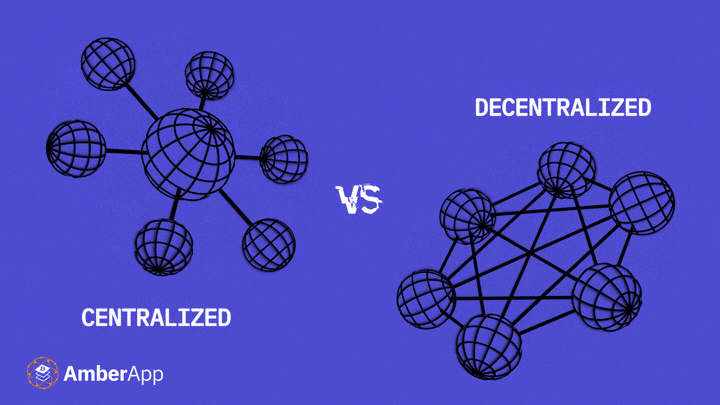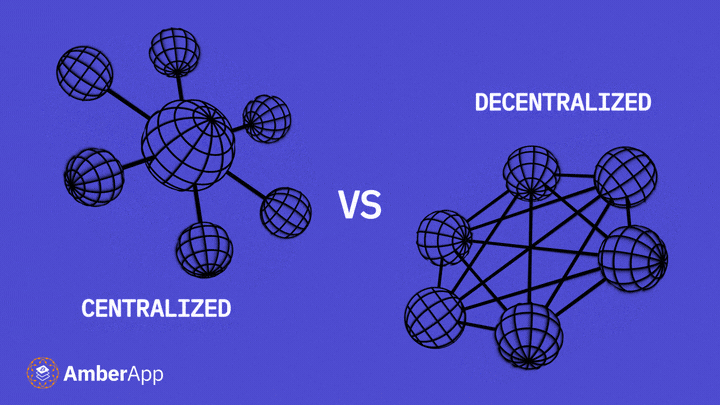
Centralisation in governance involves decision-making processes conducted by a dominant authority, such as a government or corporation, at the highest level of a top-down structure. It offers benefits such as efficiency and coordination, ensuring consistent decisions aligned with organisational objectives. Large organisations and governments often favour centralisation for coordination and decision-making.
On the flip side, extreme centralisation can lead to the concentration of power and lack of accountability. This can hinder innovation and creativity, causing organisations to stick to established practices rather than embracing new approaches. The adverse effects of centralisation can manifest in broken incentive structures and decisions that prioritise a select few over the broader interests of society. Economics in One Lesson by Henry Hazlitt is a great book for understanding more about this.
Fast as Lightning
Centralisation in Money
Centralisation in money focuses on control over the creation, distribution, and management of currency within a single entity or a small group. Historically, the shift towards centralisation occurred as economies grew, and modern banking systems and central banks emerged to increase efficiencies of trade across space. These institutions now hold the primary responsibility for money regulation in most countries.
Proponents of centralisation argue that it provides stability and control over the economy. Using various monetary policies, central banks can influence economic growth, create inflation, and respond to financial crises they themselves initiated through interventions like adjusting interest rates and injecting liquidity (aka money printing).
Critics of central banks and of centralisation more generally, however, highlight the negative consequences. Concentrated control over money can lead to an uneven distribution of power and wealth, limited transparency, and restricted participation in the economy for marginalised groups. Additionally, centralisation can impede innovation and competition in the financial sector, hindering access to innovative financial products and services, such as Bitcoin.
Conclusion
Centralisation in governance and money is a multifaceted issue with its fair share of advantages and disadvantages. While centralisation can contribute to efficiency and stability, it may also lead to power concentration and hinder progress. Striking the right balance between centralisation and decentralisation remains a significant challenge for modern societies. As history has demonstrated, absolute control over money will foster corruption and abuse, underscoring the importance of Bitcoin as a decentralised monetary policy protocol that no one human or group of humans can control.
Learn More
Do you want to learn more about Bitcoin and why money matters? Click this link to keep reading. Download the AmberApp and start stacking sats in minutes.