Bitcoin transaction fees stand as a foundational component of the network’s operational framework. Initiated by Satoshi Nakamoto upon the inception of the Bitcoin blockchain, these fees serve a crucial role: to deter spam transactions that could potentially congest and impede the network’s functionality. Transaction fees not only incentivise miners to validate transactions but also supplement the diminishing block subsidy, thereby fortifying network security by ensuring miners remain economically viable.
Exchanges and brokerages, while facilitating the buying and selling of Bitcoin, impose separate fees distinct from those required for processing transactions on the Bitcoin network. It’s vital to discern that fees charged by exchanges operate independently of the fees demanded by the network itself.
Determining the Current Bitcoin Transaction Fee
The current Bitcoin transaction fee is contingent upon the prevailing demand for block space and the willingness of users to pay. Wallets typically provide users with estimations of network fees at the time of transaction initiation, offering transparency and enabling informed decision-making.
Bitcoin transaction fees, denoted in satoshis per virtual byte (sat/vB), are critical income streams for miners, complementing the block subsidy. Users contributing fees play a direct role in upholding the security of the Bitcoin network. Following the validation of a new block, miners receive both transaction fees and the block subsidy, collectively constituting the block reward.
Transaction Fee Components
Bitcoin transaction fees are composed of several elements, each contributing to the overall fee calculation:
Transaction Size: The size of a transaction, measured in bytes, directly influences the fee. Larger transactions require more data to be processed on the blockchain, resulting in higher fees compared to smaller transactions.
Network Congestion: The level of congestion on the Bitcoin network significantly impacts fee rates. During periods of high demand, users may need to pay higher fees to ensure their transactions are prioritised by miners and included in the next block.
Fee Rate: Bitcoin transaction fees are typically denoted in satoshis per virtual byte (sat/vB). Users can choose their desired fee rate based on their urgency for transaction confirmation and prevailing network conditions.
Fee Calculation Process
The process of calculating Bitcoin transaction fees involves several steps:
- Determining Transaction Size: Bitcoin transactions consist of inputs and outputs, each consuming a certain amount of data. Inputs represent the Bitcoin being spent, while outputs denote the recipients of the Bitcoin. The size of a transaction is determined by the number of inputs and outputs, as well as additional data such as signatures.
- Estimating Fee Rate: Wallets or transaction processing platforms provide users with fee rate options based on current network conditions. Users can choose a fee rate that aligns with their desired confirmation speed and budget.
- Multiplying Fee Rate by Transaction Size: Once the fee rate is selected, it is multiplied by the size of the transaction in virtual bytes (vB). This calculation yields the total fee amount in satoshis that the user must pay to incentivise miners to include their transaction in a block.
How to save on fees by consolidating transactions
Consolidating transactions during periods of low fee environments is a smart strategy to save on Bitcoin network fees. Here’s how to do it and why it’s essential for everyone:
Wait for Low Fee Periods: Keep an eye on the Bitcoin network and wait for periods when the network is less congested. During these times, transaction fees tend to be lower due to decreased demand for block space.
Combine Multiple Withdrawals: Now, start consolidating all your transactions into a single larger withdrawal. By bundling multiple transactions into one, you reduce the number of outputs and inputs, resulting in a smaller overall transaction size and lower fees. End result is, now you have consolidated all your inputs in a single larger output and thus will help you save while spending in a high fee environment in the future.
Why it’s a Must for Everyone:
Cost Savings: Saving on transaction fees means more Bitcoin in your pocket. By adopting cost-saving strategies like consolidating withdrawals, you can maximise the value of your Bitcoin holdings.
Efficiency: Consolidating withdrawals not only saves money but also streamlines your transaction process. Instead of managing multiple small transactions, you can simplify your workflow by combining them into larger, more efficient withdrawals.
Network Health: During periods of high congestion, excessive small transactions can exacerbate network congestion and lead to higher fees for everyone. By consolidating withdrawals, you help reduce network congestion and promote a healthier, more efficient Bitcoin network for all users.
How are fees calculated in AmberApp?
At AmberApp, our goal is to provide users with a seamless and cost-effective Bitcoin transaction experience. We calculate the fees by closely monitoring network activity, and are able to provide users with fee estimates that reflect the current state of the blockchain. This dynamic approach allows us to adapt to fluctuations in demand and congestion levels, ensuring that users receive fair and competitive fee rates.
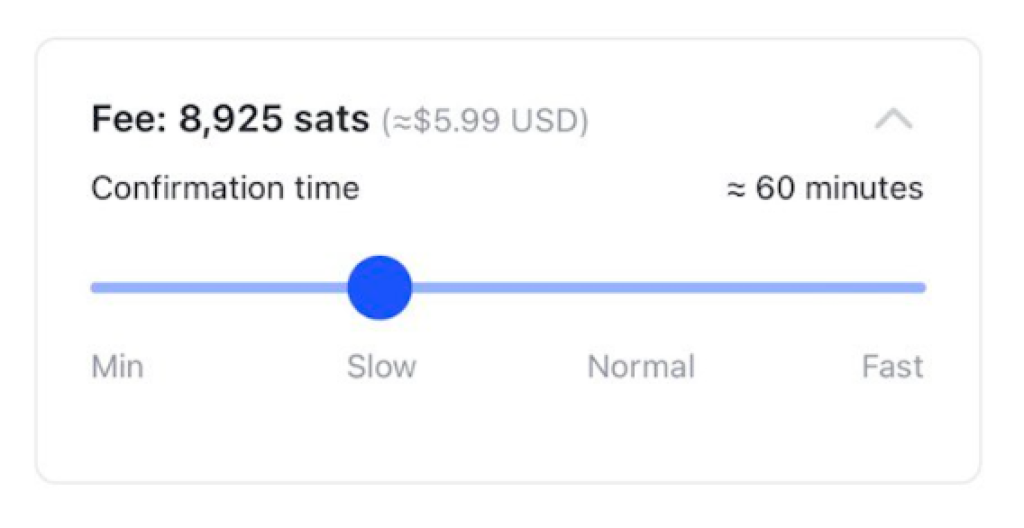
Clients have 4 options to choose from:
Minimum : Please note, at this fee rate, your transaction may take days to confirm.
Slow : Around ~60 minutes to confirm
Normal : Around ~30 minutes to confirm
Fast : Around ~15 minutes to confirm
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a layer-two scaling solution for Bitcoin that aims to address the scalability and efficiency issues of the Bitcoin blockchain. It operates as a payment protocol built on top of Bitcoin, enabling instant micropayments with low fees and high transaction throughput.
In the Lightning Network, participants create payment channels directly between each other, offloading the majority of transactions from the main Bitcoin blockchain. These channels allow users to transact with each other instantly and without incurring the fees associated with on-chain transactions.
We suggest to all our clients to explore lightning withdrawals as a way to save on fees. With lightning withdrawals, you can create an invoice for the amount you want to withdraw and paste it into the address section.
This allows you to withdraw directly via lightning, which involves lower fees compared to regular Bitcoin transactions. It’s a convenient and cost-effective option to consider when using AmberApp.
To conclude, understanding Bitcoin transaction fees and implementing cost-saving strategies is essential for maximising the value of Bitcoin holdings and promoting network efficiency. By staying informed and leveraging tools like consolidating transactions and the Lightning Network, users can navigate the Bitcoin ecosystem efficiently while minimising transaction costs.





